Innovation knows no limits
From the development of the materials to the construction of the production machines
With our know-how in the field of PTFE and ePTFE and our high standards for our products, we stand for quality – Made in Germany.
Since our company was founded in 2008, we have been constantly working on the further development of our materials and production processes in order to be able to offer our customers individual and forward-looking solutions.
expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is a specially processed form of polytetrafluoroethylene.
During processing, the PTFE molecular fibres are specifically aligned (oriented), which produces improved strength and cold flow properties in the material compared to non-oriented PTFE.
In the production of monodirectional ePTFE, the molecular fibres are oriented in one direction. The orientation increases the strength of the material in the direction of stretching.
Multidirectional ePTFE, on the other hand, is oriented in many directions. This creates a complex fibre structure that gives the material extraordinary strength and creep resistance in both longitudinal and transverse directions.
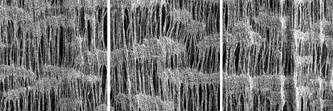
Image of the molecular fibres in monodirectionally expanded PTFE
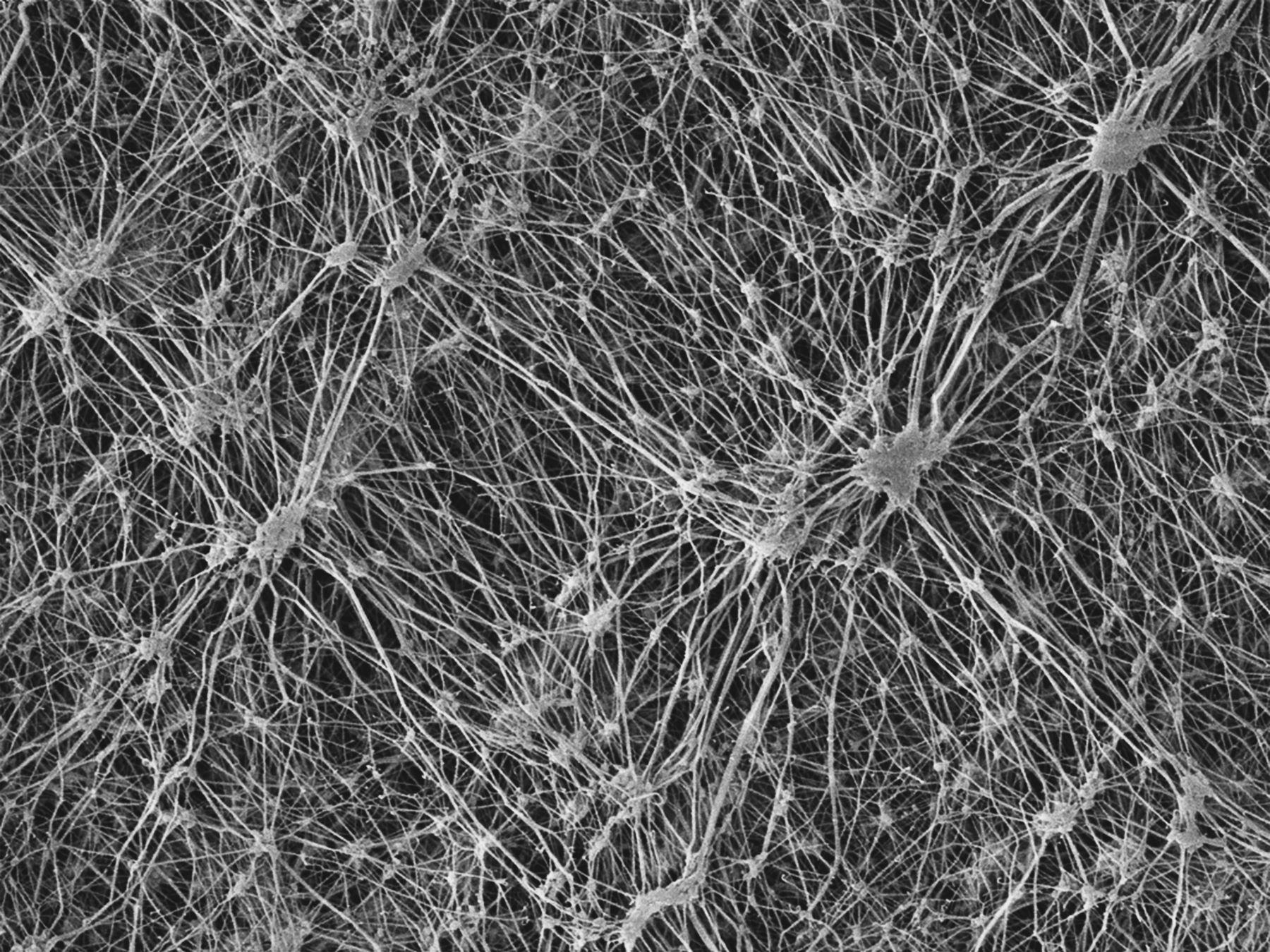
Image of the molecular fibres in multidirectionally expanded PTFE

Sintered PTFE
The ePTFE described above is usually produced by extrusion and subsequently expanded by corresponding downstream processes. This is contrasted by the manufacturing process of sintered PTFE.
In sintering, a powder or granular material is placed in a mould and then subjected to temperature and possibly pressure, which causes the individual particles to bake together. One advantage of this approach is the greater flexibility of raw materials, auxiliary materials and fillers of sintered PTFE.
In this way, sintered PTFE products consisting of
- virgin PTFE (“standard” material, unfilled and without additives)
- modified PTFE (additives and auxiliary materials to improve the material properties or processability)
- filled PTFE (mostly inorganic fillers such as e.g. SiO2 to improve certain material properties).
can be made.
Polymer chemistry
Fluoropolymers are fluorocarbon compounds, with extraordinary chemical properties and high temperature resistance.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylen)
consists solely of carbon (C) and fluorine (F) atoms, which form a helix-like molecular chain without side chains.
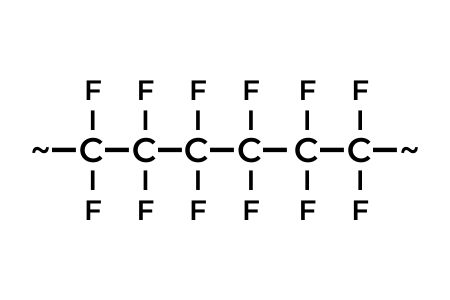
FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene)
The development of PTFE was a groundbreaking invention and a breakthrough in polymer chemistry. The unusual processing properties of PTFE, which make melt processing impossible, have led plastics manufacturers to develop a melt-processable derivative of PTFE – FEP. This new polymer, like previously known thermoplastics, could be processed as a melt using the known processes and machines. This also enabled continuous processes, such as the extrusion of FEP in the cable industry.
Although FEP is very similar to PTFE, it shows some distinct differences. It has a higher coefficient of friction, a lower continuous service temperature and is more transparent than PTFE. Gas and water vapour permeability are lower, whereas UV permeability is much higher.
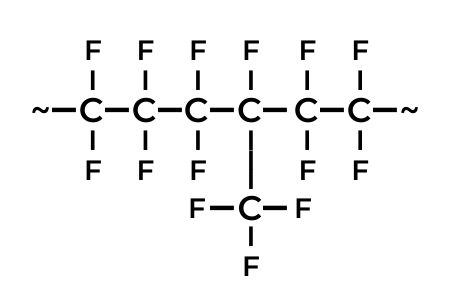
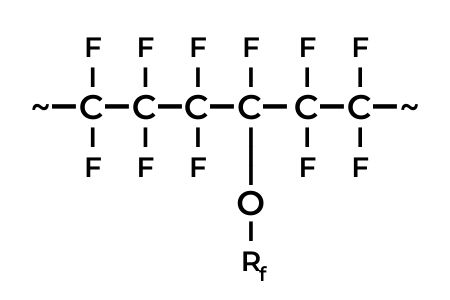
PFA (tetrafluoroethylene-perfluoro-alkoxyvinylether copolymer)
PFA was developed to improve the continuous service temperature of FEP. Due to the alkoxy side chains, PFA is meltable and thus thermoplastically processable.
You would like to know more?
Feel free to contact us, our team will be at your service quickly and competently. Either directly by mail or simply via our contact form, we look forward to hearing from you!


